
The terms SDGs, ESG, CSR, and Sustainability are frequently used synonymously, although they possess distinct meanings and ramifications within the business realm.
Here is a comparative analysis of the distinctions among these terms:
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to businesses' ethical and responsible behavior toward society and the environment. It involves the voluntary actions taken by companies to address social and environmental issues beyond their legal obligations.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) encompasses a wide range of sustainable initiatives that seek to hold businesses responsible for their effects on society, employees, shareholders, and other stakeholders. CSR is commonly regarded as the precursor to ESG practices, spearheading the movement towards enhanced social responsibility inside firms and fostering their consideration of societal effect. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a visionary and holistic approach that centers on the broader societal implications of a company's actions.
ESG refers to the three key factors that are used to evaluate the Sustainability and ethical impact of an investment or business: environmental, social, and governance.
ESG refers to a comprehensive framework employed for assessing a company's operational effectiveness in environmental, social, and governance aspects. ESG is a more precise concept compared to CSR, as it establishes specific criteria for defining the extent of impact, establishing benchmarks, and disclosing relevant data. ESG is characterized by its practical and meticulous approach, emphasizing the company's specific actions and policies. ESG is significantly more measurable and focuses on a specific framework.
Since 2016, Bursa Malaysia has mandated the disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) matters in order to enhance openness and accountability in business decision-making and operations for the benefit of investors. In the last two years, ESG has gained popularity at the expense of CSR, as indicated by Google search volume trends.
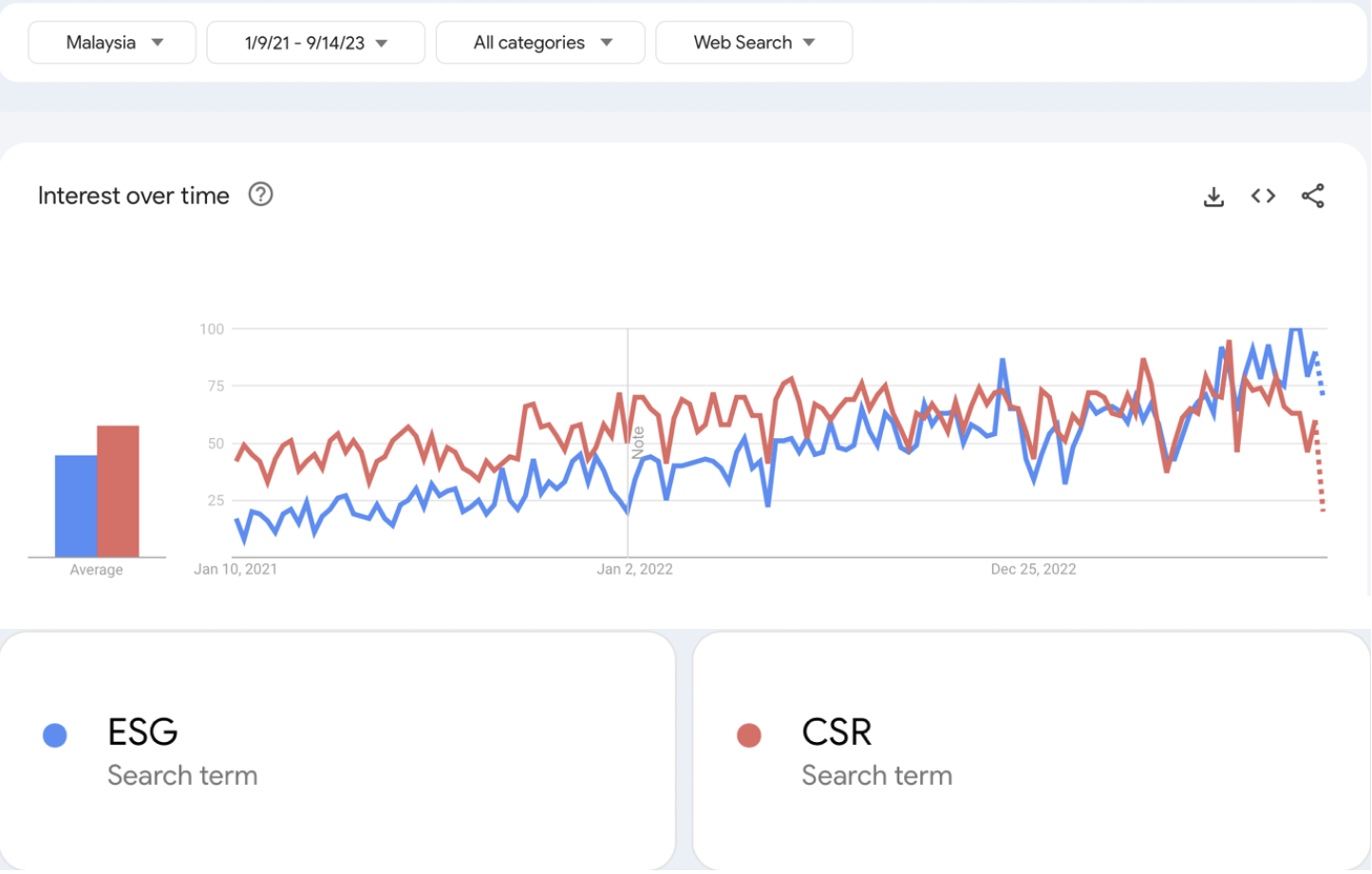
(Location: Malaysia. Time:1/9/2021-14/9/2023)
Source: Google Trend. https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2021-01-09%202023-09-14&geo=MY&q=ESG,CSR&hl=en-US
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The United Nations has established a set of 17 goals known as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with the aim of attaining a sustainable future for all. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) encompass a broad spectrum of topics, such as poverty, hunger, health, education, gender equality, clean water and sanitation, affordable and clean energy, decent work and economic growth, industry, innovation and infrastructure, reduced inequalities, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, life on land, peace, justice and strong institutions, and partnerships for the goals. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) offer businesses a framework to align their sustainability initiatives with internationally recognized objectives to address various social, economic, and environmental challenges.
Sustainability refers to the ability to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising while ensuring a balance between economic growth, environmental care, and social well-being.
The concept of Sustainability is commonly categorized into three fundamental dimensions, namely economic, environmental, and social. Within the realms of business and policy, the concept of Sustainability aims to mitigate the depletion of natural or physical resources, ensuring their enduring availability.
Sustainability encompasses and is supported by both ESG practices and CSR initiatives.
While there are notable similarities between CSR, ESG, SDGs, and Sustainability, these concepts also present distinct business difficulties and opportunities. Presented below are many strategies to mitigate ambiguity surrounding these concepts and establish a solid foundation for initiating tangible transformation:
- Understand the specific meanings of each concept and their interconnections.
- Identify the specific sectors in which your business might have the most significant impact and align your sustainability initiatives with the relevant targets.
- Develop a comprehensive sustainability strategy containing clearly defined goals, realistic targets, and quantifiable evaluations to assess developments.
- To foster support for sustainability initiatives, it is crucial to actively involve stakeholders, including business employees, customers, suppliers, and investors, in the process.
- To demonstrate a steadfast dedication to Sustainability and embrace responsibility for our activities, it is essential that we consistently and openly communicate our sustainability performance through regular reporting.

By comprehending the differences among SDGs, ESG criteria, CSR initiatives, and the concept of Sustainability, businesses can develop more efficient strategies for Sustainability and make meaningful contributions towards a sustainable future involving all stakeholders.
